Kist Valve Group introduces the core structural features of forged steel gate, globe valve and check valve, covering API 602, ASME B16.34 and other international standards, explaining the advantages of the forging process (high strength, no casting defects), split/integral body design, flange/butt-welding connection selection, pressure level control and material selection guide for oil and gas high-pressure scenarios of the valve selection reference.
First, the valve type and standard system
Forged steel valves as a key component of industrial pipelines, need to follow the domestic and international dual standard system:
- Domestic standards: JB/T 7746-2006 (compact steel valves), GB/T28766-2012 (valves for oil and gas, applicable to DN100 and below)
- International standards: API 602-2022 (oil and gas with DN100/NPS4 and the following valves), EN ISO 15761-2002, BS 5352, ASME B16.34-2017 (flange/threaded/welded valve specification)

Second, the core advantages of forged steel valves
Compared with traditional casting valves, forged steel process has significant advantages:
Elimination of casting defects: no air holes, sand holes and other problems
Enhancement of material performance: tissue fibrillation to increase the strength of more than 30
Extended service life: pressure resistance up to 25MPa
Enhanced reliability: pass rate increased to 98
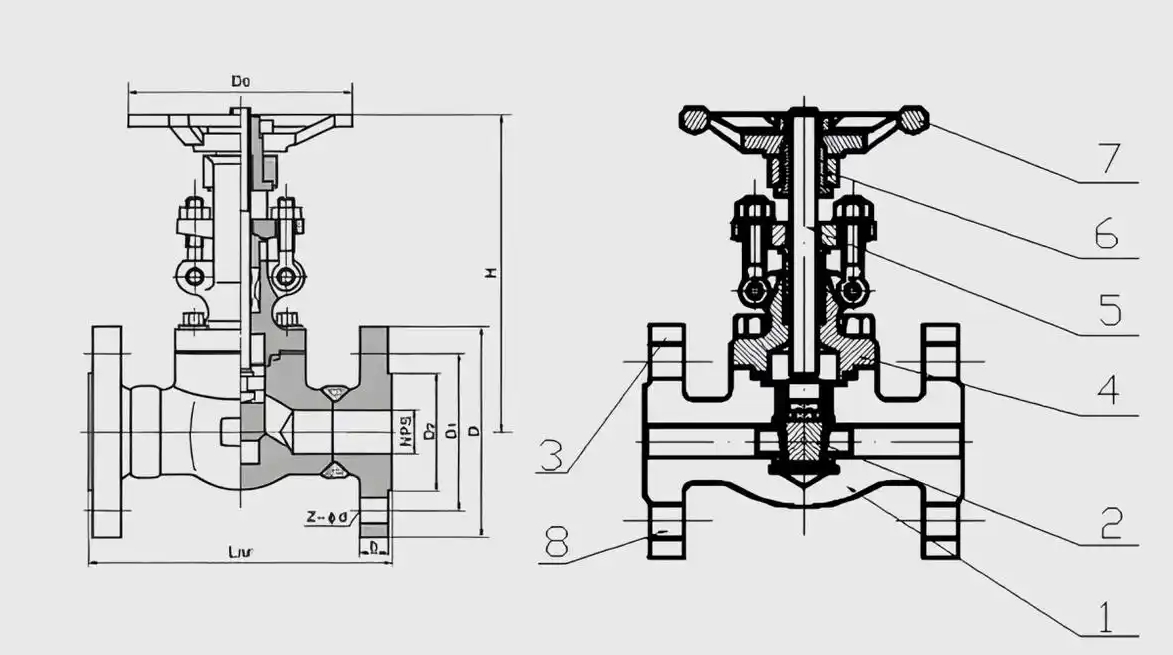
Three, flange connection structure comparison
Split welding type (economic type)
- Process characteristics: valve body and flange are forged separately and then welded together.
- Connection mode: support for threaded / socket welding / butt welding a variety of connections
- Cost advantage: reduce the die forging process, increase the material utilization rate by 25%.
- Key requirements: end flanges must be butt-welded, prohibit the use of socket welding structure
Integral forging type (high performance)
- Critical requirement: end flanges must be butt-welded, socket-welded construction is prohibited.
- Performance Advantage:
Performance advantages: 50% increase in structural reliability
Manufacturing cycle shortened by 30 percent
40% reduction of material waste
Product qualification rate of 98% or more
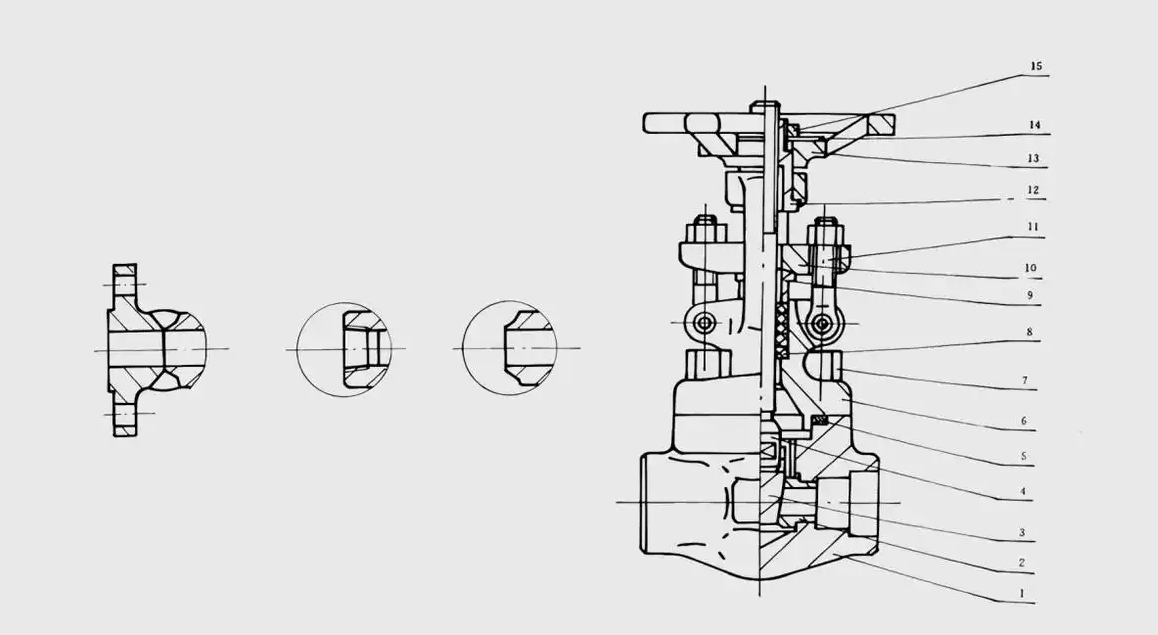
Fourth, the pipeline connection method guide
Select the appropriate connection method according to the demand of working conditions:
Small diameter pipes (DN8-DN65):
- Recommended socket welding or threaded connection
- Thread standard: 55° tapered sealing thread (GB/T7306.2-2000)
Medium and large caliber pipes (DN8-DN100):
- Preferred flange connection or butt welding connection
- Advantages of flange connection:
Eliminate the risk of weld leakage
Installation and disassembly efficiency increased by 60
Gate Valve body to realize the design of no weld
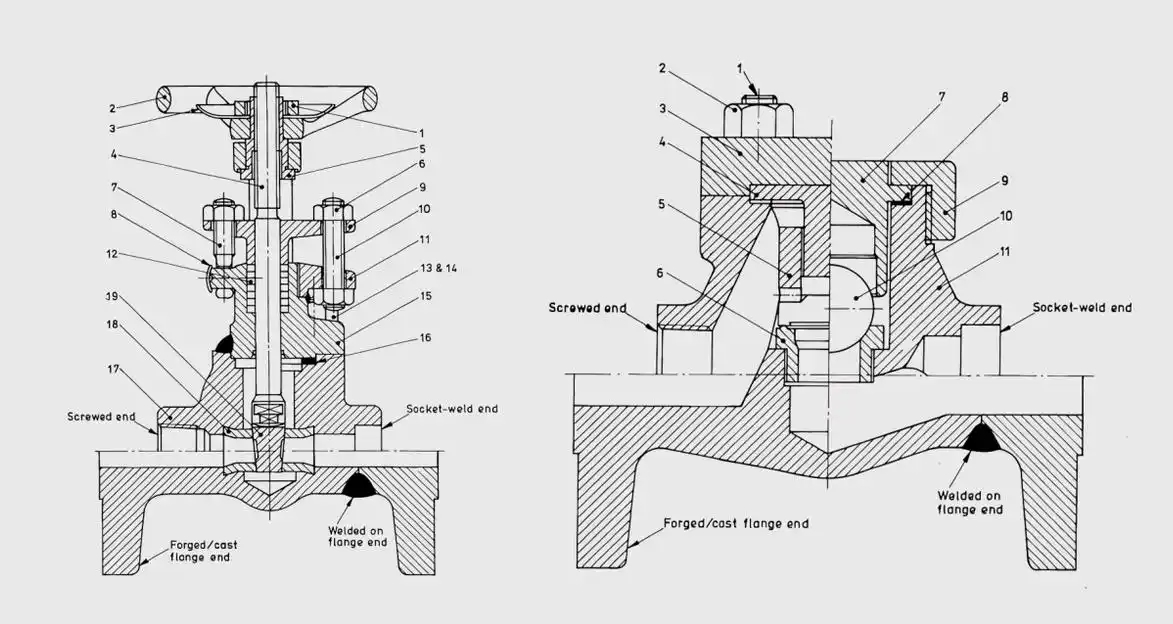
V. Pressure class comparison table
| Nominal Pressure PN | Corresponding Class | Typical Application Scenario |
| PN20 | Class150 | Atmospheric Pressure Steam / Water Supply & Drainage |
| PN50 | Class300 | Medium Pressure Oil and Gas Transportation |
| PN100 | Class600 | High Pressure Chemical Processes |
| PN140 | Class800 | Supercritical Power Generation |
| PN250 | Class1500 | Deep-sea oil and gas extraction/nuclear power plants |
Six, the valve body connection structure innovation
Valve cover connection program:
- ≤ PN140: threaded loose connector can be used
- Class1500: recommended pressure self-sealing structure
Flow path optimization design:
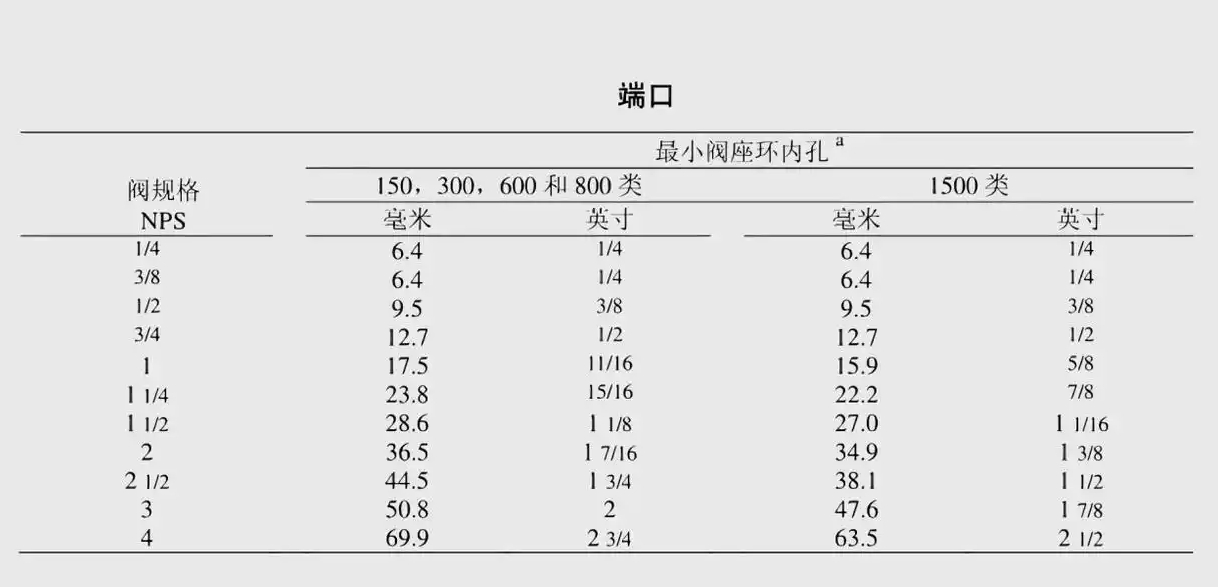
- Reduction structure application: DN25 valve seat diameter changes with pressure (17.5mm at 14MPa/15.9mm at 25MPa)
- Full bore design: GB12235/GB12234 standard valves to maintain a constant diameter of 25mm
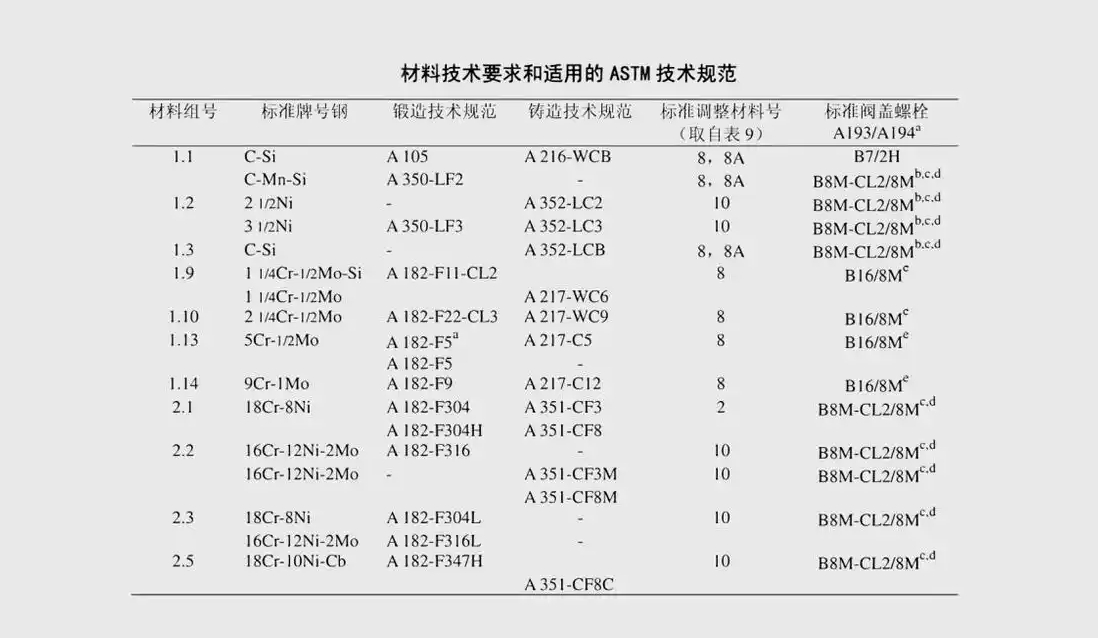
Seven, material selection reference
Commonly used forged steel material list:
Carbon steel: A105 (N), A350 LF2
Stainless steel: F304/F316 series
High temperature alloy: F91/F92
Corrosion-resistant alloy: F51/F347H
Eight, surface treatment process
Blackening treatment technology points:
Formation of Fe3O4 protective film (thickness 3-5μm)
Three core roles:
Rust protection (salt spray resistance ≥ 72h)
Appearance beautification (surface gloss Ra0.8)
Elimination of processing stress (reduce 30% residual stress)

IX. Suggestions for application areas
Suggested use scenarios:
High temperature and high pressure working conditions (≥200℃)
Corrosive media environment
Long cycle continuous operation system
Installations with high safety level requirements
This guide covers the core technical parameters of the selection of forged steel valves to help users quickly grasp the product characteristics. Practical applications need to be combined with specific operating parameters, refer to the relevant standards and specifications for selection and verification.